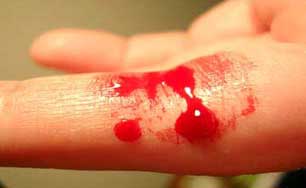
The definition of bleeding:
Bleeding is the loss of a large amount of blood outside the blood circulation.
Causes of bleeding:
1 - blood diseases such as lack of factors that help clotting (platelets).
2 - wounds and injuries.
3 - during or after surgery.
4 - result of the explosion and the bleeding blood vessel, such as bleeding from the duodenal ulcer - tuberculosis respiratory - oesophageal varices .....
. 5 - continued use of certain drugs which lead to blood thinners such as aspirin.
Bleeding complications (very important).
1 - lose blood
2 - shock = Death
3 - Pain
4 - microbial contamination
How to stop the bleeding
- How is the work of the arterial pressure?
Wrap a piece of broad cloth over twice the level of bleeding, and then make a node and then the other node, place a wooden stick or a pen and then roll the stick or pen until the closure of the artery completely.
Write the time you work pressure of the arteries, because you are removing the pressure every 20 minutes for 20 seconds until the blood passes to the injured party (to avoid gangrene).
Wrap a piece of broad cloth over twice the level of bleeding, and then make a node and then the other node, place a wooden stick or a pen and then roll the stick or pen until the closure of the artery completely.
Write the time you work pressure of the arteries, because you are removing the pressure every 20 minutes for 20 seconds until the blood passes to the injured party (to avoid gangrene).